Having a fan is a necessary aspect of any person’s life. Modern fans utilize a new technology known as Brushless DC technology (BLDC), which is implemented in a Brushless DC fan.
The induction motors used in conventional ceiling fans are powered by alternating current. However, the Brushless DC motors used by fans with BLDC technology reduce power consumption by 65% while also extending the fans’ service life.

We’ll be discussing the following information regarding BLDC Fans in length.
What is Brushless DC Motors?
A brushless DC motor is a type of synchronous motor that uses a direct current supply. It can be used to drive various types of electronic equipment, such as motors and generators. Its windings produce magnetic fields that rotate in space.
Motors that use BRUSHLESS DIRECT CURRENT are referred to as BLDC motors. Brushes and a commutator were once standard components of DC motors. It has been possible to do away with brushes in DC motors for some time now, thanks to technological advancements.
A DC-powered electric motor that doesn’t require brushes is called a Brushless Direct Current Motor (BLDC). The energy input into the motor is transformed into mechanical energy in the form of rotation.
Each BLDC motor is equipped with its own inverter power supply.
How do brushless DC motors (BLDC) differ from standard DC motors?
Commutation System:
For BLDC motors, the commutation mechanism is electronically managed (instead of the mechanical commutation system using brushes.)
Magnetic System:
Electromagnets are the magnetic system of choice for conventional fan motors. Permanent magnets, as opposed to the electromagnets found in induction motors, are at the heart of BLDC machines.
The rotor of a brushless DC motor (BLDC) contains the permanent magnets. Energy and heat are lost less frequently in the permanent magnet than in an electromagnet.
The Benefits of BLDC fans
An electronic commutator mechanism distinguishes the cutting-edge electric motor known as a brushless direct-current (BLDC) motor. Compared to induction motor fans, BLDC motor fans have several notable benefits, including:
- Due to their unique electrical construction, BLDC motor fans cannot be used in conjunction with regulators. They function through hand-held remote. The remote control allows for precise speed, timer, and even sleep settings. Because of this characteristic, it’s quite practical.
- Due to its low power consumption, fans powered by BLDC motors are ideal for use with an inverter.
- As opposed to induction motor fans, BLDC ones are more energy efficient. Compared to a standard fan, which uses roughly 80 Watts, BLDC fans only need around 35 Watts. They are the most energy-efficient fans ever discovered.
- Despite being more expensive than standard fans, BLDC fans can save annual energy costs.
- Since the BLDC motor’s magnetic fields are symmetrical rather than centered, the motor’s lifespan is increased. A regular fan will overheat eventually.
- Since there are no brushes on the rotor and the commutation is handled electronically, BLDC fans are much quieter than traditional fans.
Building a Brushless Direct Current (BLDC) Fan
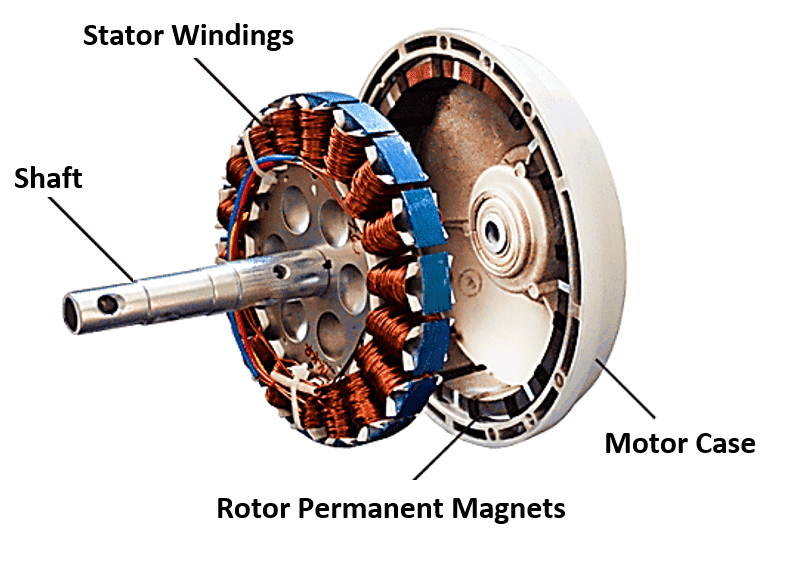
Components of a brushless DC motor:
- Stator – The copper windings inside the stator generate magnetic flux when an electric current is sent through it, making it a key component in an electric motor.
- Rotor – The revolving item, known as a rotor, is equipped with permanent magnets.
- Shaft – It is the rod that runs from a motor to the program.
- BLDC Drive – This motor’s controller is built into the drive itself.
Toiling away at BLDC Fan
Brushless-dc motors have a rotor with a permanent magnet connected to it that spins around a stator with electromagnetic coils and some control electronics.
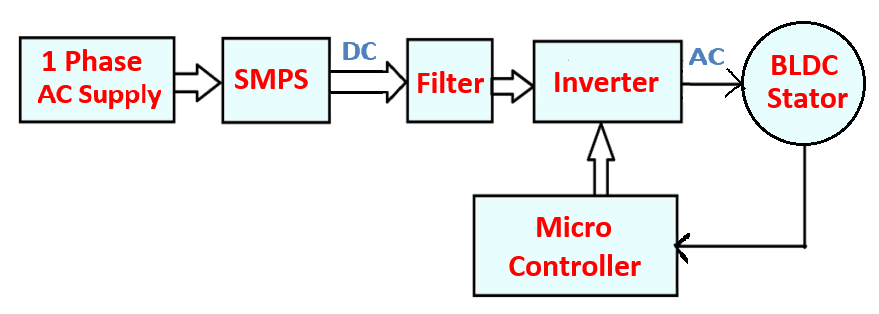
The BLDC Drive controls the rotation of the BLDC fan. In order to understand how the BLDC drive functions, consider the following.
The following items make up a BLDC drive.
1. Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS)
An SMPS’s primary function is to supply clean, consistent power to the BLDC drive. The purpose of the circuitry in a switched-mode power supply is to convert an uncontrolled AC voltage into a regulated DC voltage. In this case, an SMPS is employed to change the DC power from the AC power.
2. Microcontroller
Data is received from a remote control and processed by a microcontroller before being sent on to an inverter.
3. An inverter
An inverter is a piece of electrical equipment that converts DC current into AC current (AC). With input from the microcontroller, the inverter then supplies power to the motor.
The motor’s permanent magnet rotor blows air through fan blades.
Exactly how a Brushless DC Drive Functions
To put it simply, when we switch on a BLDC fan, the SMPS converts the AC power to DC supply, the microcontroller receives the input signal from the remote control, and the inverter drives the BLDC motor based on the input signal.
As can be seen in the diagram below, the BLDC supplies power to a closed-loop Microcontroller via an inverter.
A uniform field in the air gap is generated when the stator coils are supplied with power, transforming the stator into an electromagnet. The inverter switching transforms the DC supply into a trapezoidal AC voltage waveform.
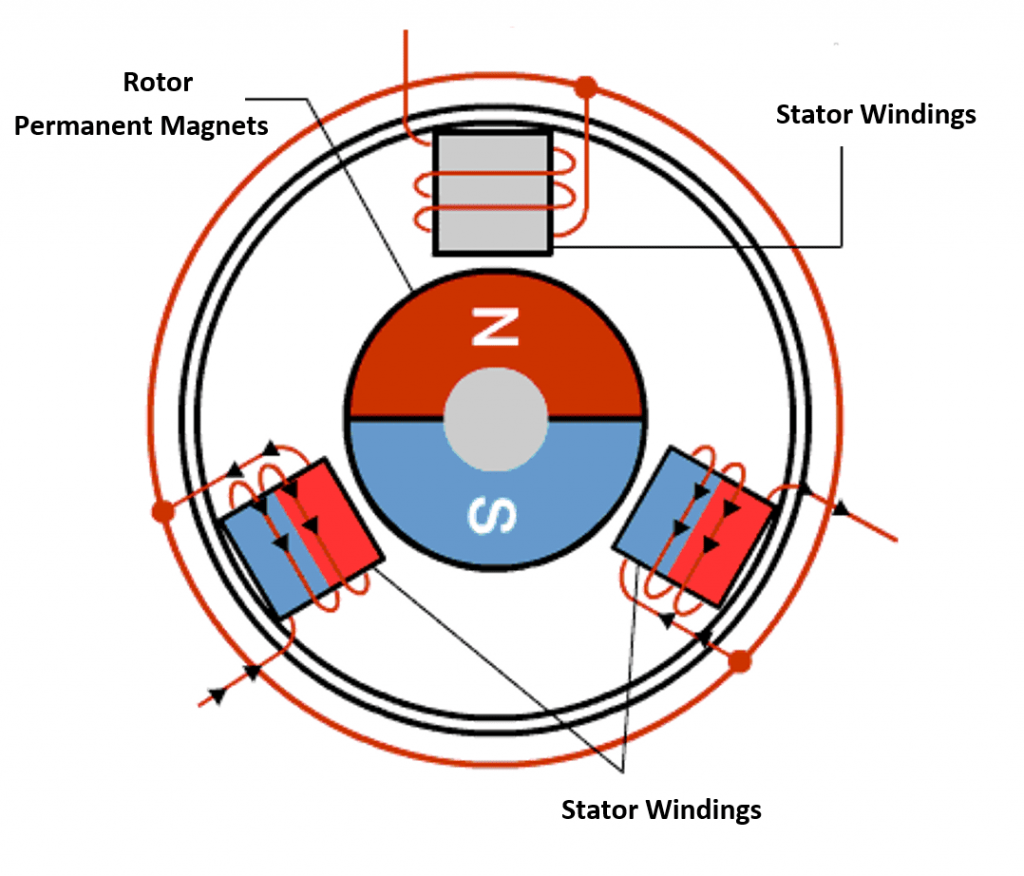
The rotor keeps turning because of the attractive force between the electromagnet stator and the permanent magnets in the rotor. Windings are switched between High and Low signals, and their corresponding electrified poles are the North and South terminals. The rotor is pushed to rotate by magnetic force when the rotor and stator have the same polarity (e.g., S and S, N and N).
By maintaining a consistent polarity between the rotor and stator, rotation may be kept going in the rotor at all times. When the rotor’s North and South poles line up with those of the stator, the motor starts to turn.
